Farm records play a vital role in modern agricultural management. These documents track activities, finances, resources, and outcomes on a farm.
Accurate records help farmers make informed decisions, plan for the future, and meet legal and financial requirements.
This article explains what farm record means, how it is used in agriculture, the types farmers keep, and how technology supports recordkeeping.
What Is Farm Record?

A farm record is documentation of all key activities, facts, and events that occur on a farm over time. These records capture crop production, livestock care, expenses, income, inputs used, and other operational details.
Also read: Essential Farm Tools and Their Uses You Must Know
They show what has happened, when it happened, and how resources were used.
Farm records may exist in paper books, digital files, or database systems. They serve as a historical archive and a planning tool for managing farm operations.
Why Are Farm Records Important in Agriculture?
Farm record in agriculture provides a factual basis for decision-making and business planning. Accurate records help farmers:
- Plan future activities based on past performance.
- Track income, expenses, and profitability.
- Prepare tax reports and meet legal requirements.
- Apply for loans or financial support using documented performance.
- Improve resource use and operational efficiency.
Well-kept records make farm management more transparent and reliable.
Basic Elements of Farm Records
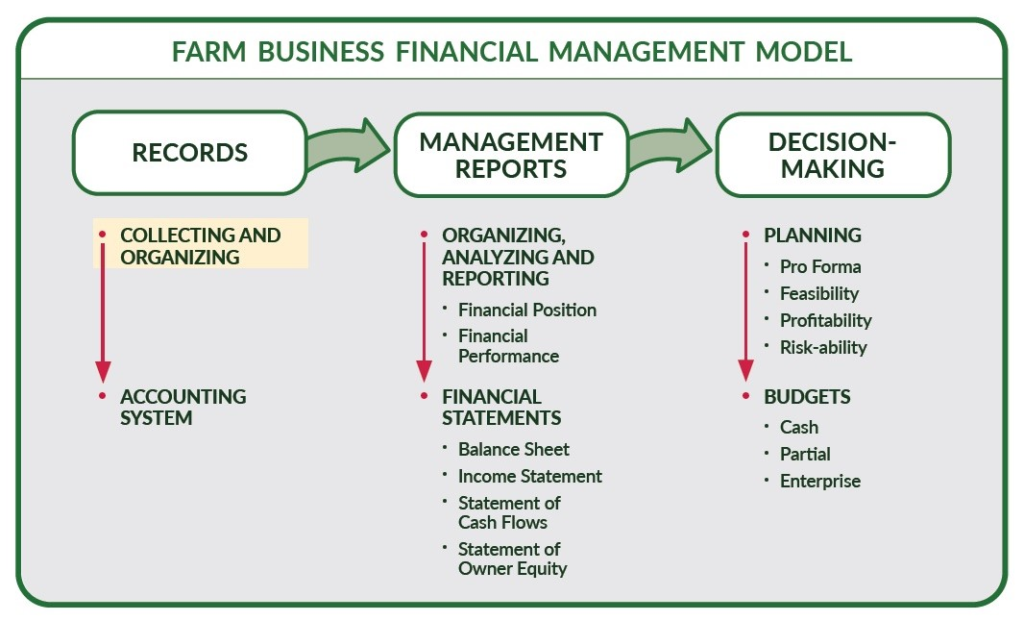
Farm records typically include data on:
- Production outputs such as crop yields or livestock products.
- Financial transactions including sales, purchases, and expenses.
- Inputs like seeds, fertilisers, feeds, and chemicals.
- Labor events and equipment use.
These elements help managers track what resources were used and the results achieved.
What Is Farm Record in Agriculture?
Farm record in agriculture refers to all documented information used to monitor and evaluate agricultural business operations. Records show the chronology of actions and transactions on a farm and provide a basis for analysis.
In agriculture, both production and financial records are essential. Production records cover physical output and resource use. Financial records cover money in and out. Both give clear insights into farm performance.
What Is Farm Input Record?
A farm input record is a type of documentation that tracks the inputs used on the farm. These inputs include seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, feed, tools, and machinery usage.
Farm input records record quantities purchased, used, and stored. They may also show costs and application dates. Keeping these records helps farmers assess input efficiency and control expenses.
Also read: The Ultimate Importance of Agriculture for Students & Society
What Are the Types of Farm Record?
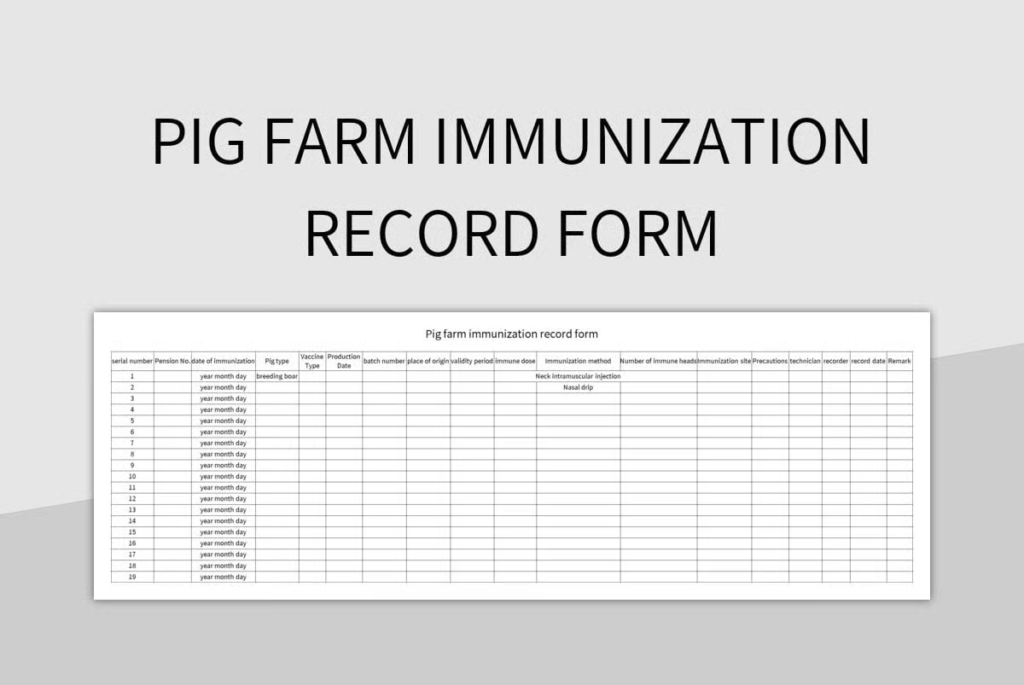
Farm records are often organised into specific types based on their focus or purpose. Farmers keep different categories to simplify management and reporting.
Farm Diary
A farm diary records daily activities and events on the farm. It may show planting dates, animal births, pesticide applications, and other routine details. These records help track past activities and plan future ones.
Farm Inventory
A farm inventory lists all the assets owned or used on the farm. This includes tools, machinery, buildings, livestock, and stored products. Inventory records help farmers know what resources are available.
Production Records
Production records cover all output from crops or livestock. These records may be kept weekly, monthly, or annually. They enable farmers to compare performance over time.
Sales Record
Sales records document what was sold, the quantities, prices, and dates. These records help calculate income and assess profitability.
Consumption Record
Consumption records track products consumed by the farmer, family, or workers. They differentiate between what was sold and what was used on the farm.
Labour and Worker Records
Labour records show details of workers, wages, and labour costs. These help manage labour expenses and plan workforce needs.
Expenditure and Financial Records
These records list all farm expenses, such as utility bills, input costs, maintenance, and other operating costs. They help with budgeting and financial analysis.
Vehicle and Equipment Records
These records track vehicles and equipment usage, repairs, service dates, and fuel consumption. They help manage the upkeep of assets.
Farm Recordkeeping Templates & Samples
Templates help farmers structure and standardise their farm records. A typical farm recordkeeping format includes sections for farm identity, production records, labour records, and input details.
For example, a production record template may list dates of activities, type of crop or livestock, and quantities produced. A labour record form might capture worker names, dates worked, and total hours.
In some jurisdictions, downloadable recordkeeping templates are available for specific tasks such as agricultural chemical use, spray applications, or veterinary treatments. These templates ensure compliance with safety or legal requirements.
Using templates helps farmers keep consistent information and makes it easier to organise and retrieve data when needed. Click the button below to access to a list of templates you could use.
What Is Computer Aided Farm Record?

A computer aided farm record system uses software tools to manage farm data electronically. These systems automate entry, storage, and retrieval of farm records.
Computer aid can include spreadsheets, dedicated farm management software, or digital databases. Digital systems reduce manual errors and make analysis faster.
Benefits of Computer Aided Farm Record
Electronic recordkeeping offers several benefits:
- Ease of use: Automated calculations save time.
- Improved accuracy: Software reduces manual errors.
- Faster reporting: Digital systems produce summaries quickly.
- Remote access: Information can be shared online.
These advantages make it easier for farmers to analyse large amounts of data and plan for future seasons.
Electronic Tools Used in Farm Recordkeeping
Farmers use various electronic tools, such as:
- Spreadsheets like Excel or Google Sheets.
- Farm accounting and management software.
- Mobile apps and cloud databases.
These tools help organize records for easy retrieval and analysis.
How Farm Records Support Decision-Making
Farm records provide a factual basis for decisions. They allow farmers to evaluate what works and what does not. For example, examining yield records helps a farmer choose the best crop varieties.
Comparing input costs over time helps select more efficient suppliers. These analyses support better planning and profitability.
Legal and Financial Compliance
Farm record keeping may be required by law in some jurisdictions. Records support accurate tax reporting, safety audits, and environmental compliance. They also help farmers meet lender or insurer requirements when seeking credit or coverage.
Best Practices for Farm Record Keeping
Some best practices include:
- Organize records into clear categories.
- Update records consistently.
- Back up digital data regularly.
- Use standard templates or software tools.
These practices help ensure records stay accurate and useful.
Challenges to Effective Farm Record Keeping
Keeping detailed farm records can be difficult for many farmers. One common challenge is limited knowledge or training in recordkeeping methods. Some farmers lack awareness of how to organise and interpret data, leading to incomplete records.
Another challenge is the time and labour required to record data. Farming activities already demand significant effort, so recording details consistently can feel burdensome, especially on larger farms.
In addition, low access to technology or digital tools can hinder recordkeeping. Where farmers rely on manual notebooks or don’t have a reliable way to store digital data, records may become disorganised or lost.
These challenges can reduce the accuracy and usefulness of farm records, making it harder to support decision-making and planning.
Farm Records and Risk Management
Farm records play a significant role in risk management in agriculture. Farmers use detailed records to identify patterns and potential issues before they become costly problems.
For example, records of weather events, pest outbreaks, or input use can help farmers anticipate recurring challenges and plan accordingly. Accurate financial records also help farmers prepare for lean seasons or unexpected expenses by identifying weak points in cash flow.
Recordkeeping supports long-term decision-making and business sustainability by providing historical data to compare against new conditions. This reduces uncertainty and supports strategic planning.
Future of Farm Recordkeeping (Technology Trends)
The future of farm recordkeeping is closely tied to digital agriculture and emerging technologies. Digital agriculture uses electronic data collection, storage, analysis, and sharing to optimise farm operations.
Increasingly, farmers use smart farm management systems that combine data from sensors, GPS, and software tools to automate recordkeeping. These technologies help reduce manual data entry and improve accuracy.
Precision agriculture, which is part of this technological shift, uses real-time monitoring and data-driven insights to refine decisions on inputs like water, fertiliser, and labour. This supports crop and livestock production efficiency.
As digital tools continues to change, farm records will increasingly include real-time data from machinery and environmental sensors, enabling more timely risk assessment and operational adjustments.
Summary
- Farm records are the foundation of efficient agricultural management
- They document activities, inputs, outputs, and financial transactions
- Farmers use records to make informed decisions, meet regulations, and plan for profitability
- Electronic or computer-aided systems improve ease and accuracy of data handling
- Detailed, well-organized records benefit farms of all sizes
Conclusion
Farm records form a fundamental element of successful agricultural management. These records document what happens on a farm, including production, inputs, finances, and operations.
Accurate farm record keeping allows farmers to evaluate performance over time, track income and expenditures, and make informed decisions for future planning and budgeting.
Keeping detailed records also supports legal compliance, risk management, and access to financial services such as loans.
In modern agriculture, systems like computer aided farm record tools help organise data efficiently and improve accuracy. Whether in digital or manual form, consistent recordkeeping enriches a farmer’s understanding of their business and strengthens farm viability.
Overall, maintaining reliable farm records supports better planning, more effective use of resources, and improved long-term outcomes for agricultural enterprises.
Would you like to explore more content like this? Turn on notifications for new posts and follow us on X (formerly Twitter), @snehtv.








